American Black Bear: hereâs the scoop
threats
In general black bear populations are increasing, but they continue to be threatened in certain areas by habitat destruction, poaching and motor vehicle accidents.
Committed to Conservation
The Buttonwood Park Zoo participates in the Association of Zoos and Aquariums Species Survival Plan (SSP) for Black Bears. Instead of focusing on breeding and genetic diversity, the Black Bear SSP manages the placement of rescued and rehabilitated bears that cannot return to the wild.
Species
American Black Bear
Scientific name
Ursus americanus
Habitat
Temperate and boreal forests, but they also range into subtropical areas of Florida and Mexico as well as into the subarctic
Diet
Omnivorous and opportunistic feeders, black bears diet changes depending on their location and the season. Plants, fruits, nuts, insects, fish, small mammals, carrion and human-related food are all part of their diet
Life Expectancy
20 – 30 years
Did you know?
American black bears can hibernate for up to seven months in the northern portions of their range, considerably shorter periods in more southerly areas and may skip it all together in warm climates where food in abundant year-round.
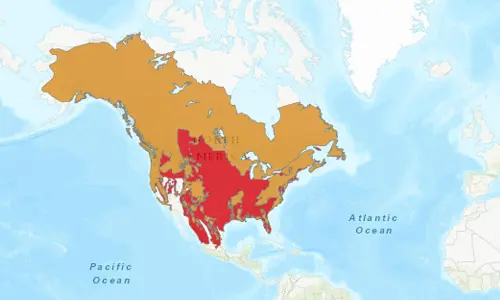
Range
Canada, United States and Mexico
The color red represented in the map refers to where black bears are no longer found
Conservation status
Least Concern
Widespread and abundant